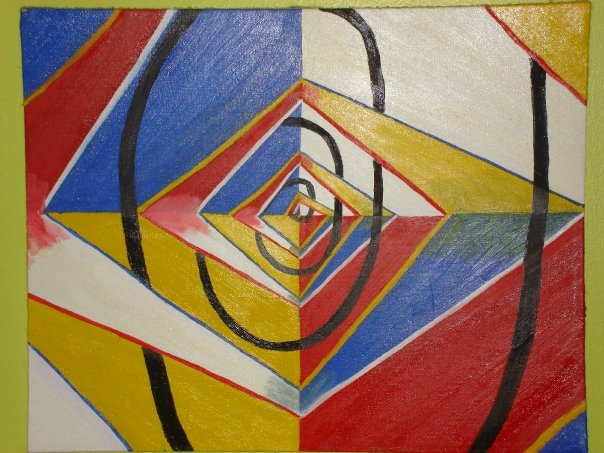
This piece of the Interdependence series was an effort to take the image portrayed in the broad view of Interdependence: the Overview and zoom in on the individual concepts to illustrate the interplay of the four seasons, especially as they pertain to our perception, what is really happening, and our own existence with regard to that.
Strangely enough, even 15 years after painting it, meditating on it, and really exploring these concepts in depth; they are still difficult to really put into words. I guess I should spend more time with them…you know what they say. “If you don’t know it well enough to teach it, then you don’t really know it.
Since I am struggling with it, I will leave you with the image, and some words on reality and perception as a computer perceives them.
The interplay of reality and perception with regard to interdependence is a complex and fascinating topic, encompassing how our understanding of the world is shaped by our interactions with others and how our collective perceptions can, in turn, influence reality.
Reality and Perception
Reality refers to the state of things as they actually exist, independent of human interpretation or perception. It encompasses the objective truths about the world, including physical laws, events, and facts that remain constant regardless of individual beliefs or opinions.
Perception, on the other hand, is the process by which individuals interpret and make sense of sensory information. Perception is inherently subjective, shaped by personal experiences, cultural background, cognitive biases, and social influences. What one person perceives may differ significantly from another’s interpretation of the same reality.
Interdependence
Interdependence refers to the mutual reliance between individuals, groups, or entities, where the actions and outcomes of one party affect and are affected by others. In social and psychological contexts, interdependence highlights how our thoughts, behaviors, and experiences are influenced by our interactions with others.
Interplay of Reality and Perception in Interdependence
- Social Constructivism:
- Social constructivism posits that much of what we consider reality is constructed through social interactions and shared perceptions. For instance, societal norms, values, and institutions are products of collective agreement and belief. The concept of interdependence is central here, as our perceptions are continuously shaped by our interactions with others, and these shared perceptions can solidify into what we accept as reality.
- Feedback Loops:
- Interdependence creates feedback loops between reality and perception. For example, if a community collectively perceives a certain area as unsafe, this perception can influence behavior, such as reduced foot traffic or increased security measures. Over time, these behaviors can alter the actual conditions of the area, potentially making it less safe and thus reinforcing the original perception.
- Cultural Influence:
- Cultural interdependence shapes reality and perception through shared beliefs and practices. Cultural narratives and myths, such as the legend of the Loch Ness Monster, illustrate how collective perceptions can give rise to a shared reality that influences behavior, tourism, and even local economies. These perceptions, although they may stem from subjective beliefs, can create tangible effects in the real world.
- Cognitive Bias and Group Dynamics:
- Cognitive biases, such as confirmation bias, are magnified in group settings, where interdependence can lead to groupthink. In such scenarios, individuals may conform to the perceived reality of the group, even if it contradicts objective evidence. This dynamic demonstrates how interdependence can sometimes distort reality, as collective perceptions override individual critical thinking.
- Scientific and Technological Advancements:
- Interdependence in scientific communities exemplifies the positive interplay of reality and perception. Peer review and collaborative research ensure that individual perceptions are scrutinized and refined through collective effort, bringing perceptions closer to objective reality. This interdependence fosters a more accurate understanding of the world.
- Media and Information:
- The media plays a crucial role in shaping perceptions of reality. News reports, social media, and other communication channels create a shared narrative that can influence public opinion and behavior. The interdependence between media producers and consumers means that perceptions can rapidly shift, altering the perceived reality of events, issues, and phenomena.
Conclusion
The interplay of reality and perception, particularly through the lens of interdependence, highlights the dynamic relationship between how we understand the world and how we interact with others. Our perceptions are not isolated constructs but are continually influenced by our social connections and interactions. This interdependence means that while we strive to comprehend objective reality, our collective perceptions can shape and sometimes even create aspects of the reality we experience. Understanding this interplay can help us navigate the complexities of social interactions, cultural norms, and collective beliefs with greater awareness and critical insight.